Many Fortune 500 organizations are adopting AWS to deploy Java applications services, however, Cloudera Enterprise makes it possible for organizations to deploy the Hadoop clusters in the AWS cloud.
According to one of the trusted Business media, ‘Running Cloudera Enterprise on AWS provides the greatest flexibility in deploying Hadoop – while providing robust security, governance, and data management.’
AWS Overview
Cloudera Enterprise build can use the following service providing:
1) Elastic Compute Cloud (EC2)
Amazon EC2 provides a wide selection of instances optimized to fit different use cases.
It consists of:
- On-Demand Instances
- Reserved Instances
- Spot Instances
2) Simple Storage Service (S3)
S3 is designed for 99.999999999% durability and availability. It is a crucial component of AWS Data Lake.
3) Relational Database Service (RDS)
Relational Database Service (RDS) provides users to provide various kinds of supported relational database instances, connecting Oracle and MySQL. RDS manages database management tasks, such as backups for a user-defined retention period, point-in-time recovery, patch management, and replication, allowing users to pursue higher value software application development or database refinements.
4) Virtual Private Cloud (VPC)
Virtual Private Cloud is an isolated environment created for managing Hadoop, clusters, and Applications in the cloud.
With VPC, we can create multiple subnets in different Azs.
Deployment Architecture
This section describes Cloudera’s recommendations and best practices applicable to Hadoop cluster system architecture.
Instance Types & Resource Planning
Cloudera recommends deploying these instance types into production:
- Compute Optimized – Used for process-centric applications, Image Processing
- Memory Optimized – Used for in-memory processing, Spark applications
- Storage Optimized - Used for storage management
- General Purpose – Used for general purpose
- Accelerated Computing (GPU) – Used for gaming, 3D visualization
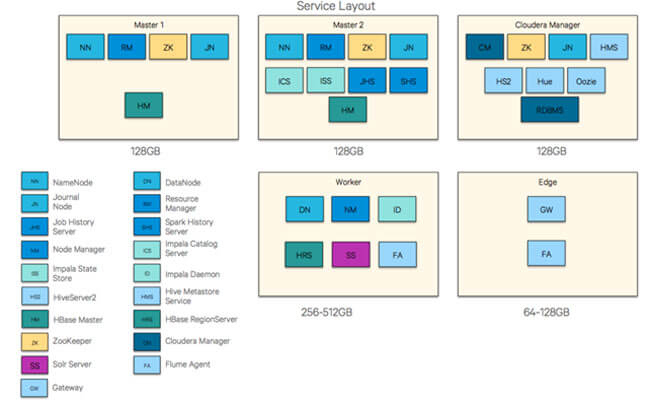
Hosts & Services Layout
- Master Nodes
- Worker Nodes
- Utility Nodes
- Edge Nodes
Master Nodes
- ResourceManager
- NameNode
- Standby NameNode
- JournalNodes
- ZooKeeper
Worker Nodes
- HDFS DataNode
- YARN NodeManager
- HBase RegionServer
- Impala Daemons
- Solr Servers
Utility Nodes
- Cloudera Manager
- Cloudera Management Services
- JournalNode
- ZooKeeper
- Oozie
- Hive Server
- Impala Catalog Server
- Impala State Store
- Job History Server
Edge Nodes
- Third-party tools
- Hadoop command-line client
- Hive command-line client
- Impala command-line client
- Flume agents
- Hue Server
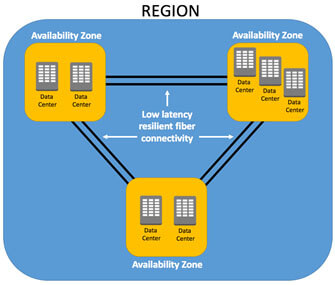
Regions and Availability Zones
Regions
Regions are completed in geographical locations where AWS services are built.
Availability Zones
AZ is a fully isolated infrastructure with one or more data centers. Each AZ has independent power, cooling, and physical security and is connected via redundant, ultra-low-latency networks.
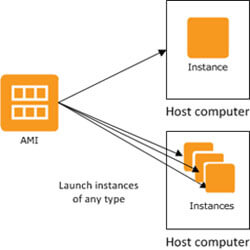
Amazon Machine Image (AMI)
Amazon Machine Images (AMIs) are the virtual machine images that run on EC2 instances.
AMI is a template that contains a software configuration including an operating system, an application server, and applications.
For launching EC2 instances, AWS provides multiple options:
- AWS Marketplace
- Community AMI
- My AMI
Cloud Storage Options
1) Object Storage (S3)
Unlike HDFS, S3 is Enterprise storage that stores unlimited data and offers industry level security, data availability.
S3 offers you robust capabilities to support access, price, replication, and data protection.
The data on S3 is organized and stored in the form of BUCKETS.
You can access data in the bucket using below S3 Storage classes:

2) Elastic Block Storage (EBS)
Amazon Elastic Block Store (Amazon EBS) gives block-level cache volumes for use with EC2 instances.
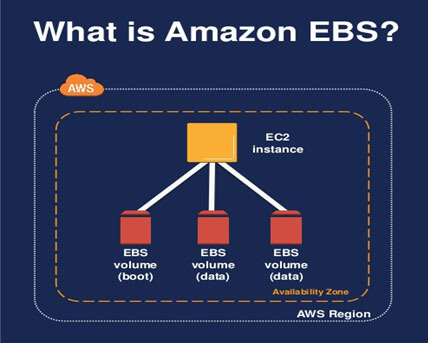
EBS Volume types:
- SSD-backed volumes – It is analyzed for transactional workloads improving periodic read/write activity with small I/O size, where the dominant performance approach is IOPS
- HDD-backed volumes – It is optimized for large streaming workloads where throughput is a better performance measure than IOPS
3) Enterprise Relational Database
Cloudera Enterprise deployments require relational databases for the following components: Cloudera Manager, Cloudera Navigator, Hive megastore, Hue, Sentry, Oozie, and others.
On the AWS cloud, you can find this Relational DB with AWS RDS.
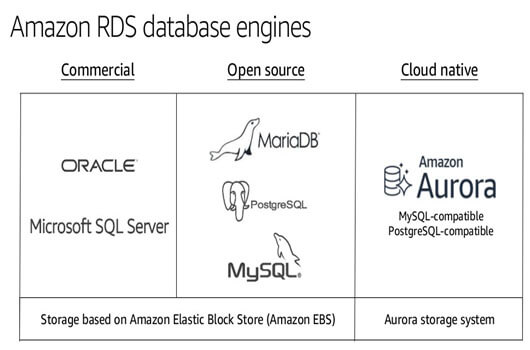
AWS RDS
Relational DB service (RDS) is a fully-managed AWS service with a choice of popular Database engines.
Cloudera supports the following Enterprise Databases:
- MySQL
- Oracle DB
- MariaDB
- Postgre DB
Deployment Topologies
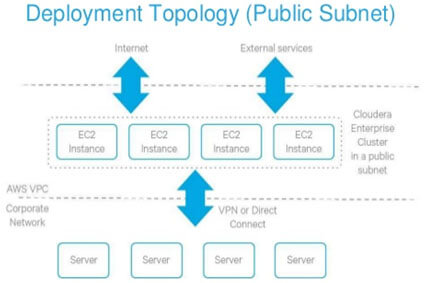
1. Cluster inside a public subnet in VPC
A public subnet in this context is a subnet with a route to the Internet gateway. Instances provisioned in public subnets inside VPC can have direct access to the Internet as well as to other external services such as AWS services in another region.
2. Cluster inside a private subnet in VPC
Instances provisioned in private subnets inside VPC don’t have direct access to the Internet. However, instances must go through VPC endpoints to reach AWS services and NAT for the internet.




